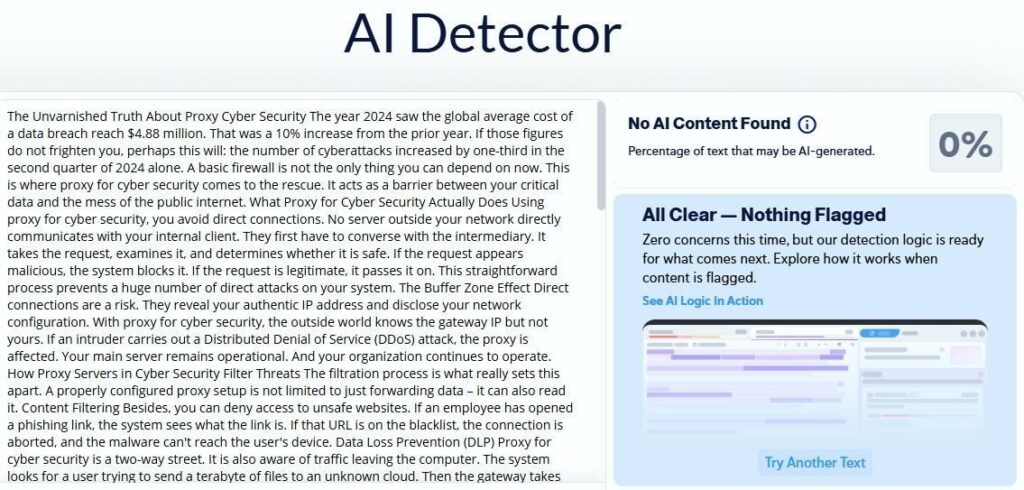
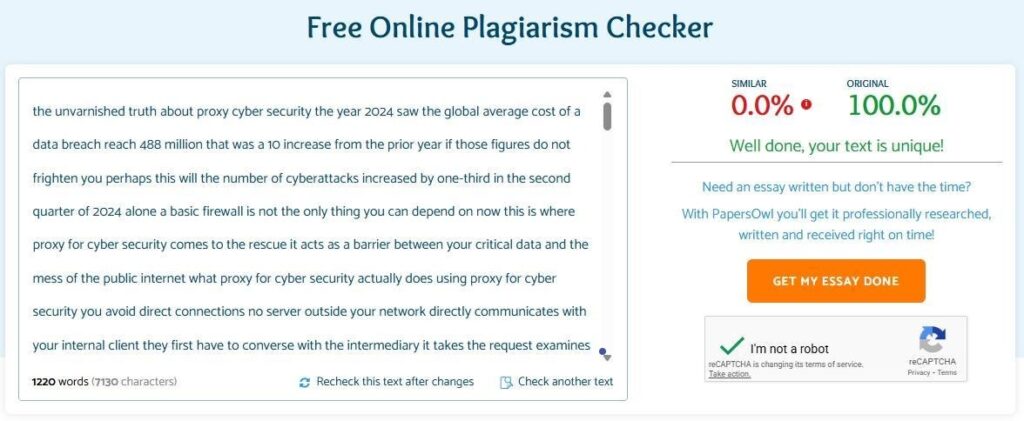
The year 2025 saw the global average cost of a data breach reach $4.88 million. That was a 10% increase from the prior year. If those figures do not frighten you, perhaps this will: the number of cyberattacks increased by one-third in the second quarter of 2025 alone. A basic firewall is not the only thing you can depend on now. This is where proxy for cyber security comes to the rescue. It acts as a barrier between your critical data and the mess of the public internet.
What Proxy for Cyber Security Actually Does
Using proxy for cyber security, you avoid direct connections. No server outside your network directly communicates with your internal client. They first have to converse with the intermediary. It takes the request, examines it, and determines whether it is safe.
If the request appears malicious, the system blocks it. If the request is legitimate, it passes it on.
This straightforward process prevents a huge number of direct attacks on your system.
The Buffer Zone Effect
Direct connections are a risk. They reveal your authentic IP address and disclose your network configuration.
With proxy for cyber security, the outside world knows the gateway IP but not yours. If an intruder carries out a Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) attack, the proxy is affected. Your main server remains operational. And your organization continues to operate.
How Proxy Servers in Cyber Security Filter Threats
The filtration process is what really sets this apart.
A properly configured proxy setup is not limited to just forwarding data – it can also read it.
Content Filtering
Besides, you can deny access to unsafe websites. If an employee has opened a phishing link, the system sees what the link is. If that URL is on the blacklist, the connection is aborted, and the malware can’t reach the user’s device.
Data Loss Prevention (DLP)
Proxy for cyber security is a two-way street. It is also aware of traffic leaving the computer.
The system looks for a user trying to send a terabyte of files to an unknown cloud. Then the gateway takes notice and prevents the transfer. This stops data theft, which can be even more harmful than an external breach.
Selecting the Right Tool
Proxies differ, so you need to pick the right one for the task.
Datacenter
Cheap and fast. The IP addresses are provided by the cloud service.
- Best use: High-speed scraping, routing of internal traffic.
- Weakness: Websites can easily spot and often block the whole subnets of datacenter IPs.
Residential
These IPs are assigned to users’ devices by Internet Service Providers (ISPs). They disguise themselves as ordinary Internet users.
This is a very important point for security researchers. If you need to do a background check on a threat actor or collect data from a phishing site without them knowing, you have to act like a regular victim. A good residential proxy allows your security team to access threat intelligence without being blocked or misled.
Reverse
These are located directly in front of your web servers. They balance the load and manage the encryption. Proxy for cyber security heavily relies on reverse IP addresses to cleanse incoming traffic before it reaches your application database.
The Economics of Proxy for Cyber Security
The price of security tools is not a joke, but these solutions offer flexible pricing models.
Generally, you would have to pay either by bandwidth or per IP.
- Residential: These are high-priced. You will have to pay between $3 and $15 per GB. If you purchase in small quantities, high-end providers may charge up to $20.
- Datacenter: These are much, much cheaper. You can find these for only $0.50 per IP or $0.10 per GB.
- ISP: This is a middle path. ISPs are faster than residential ISPs, but the block is harder than the datacenter block. So, expect around $1.50 per IP.
Now compare $15 per GB to the $4.88 million price tag of a breach. The math works out.
Implementing Protocols
In addition to buying the IP, you also have to properly configure it.
Proxy server security demands strict rules:
- Authentication: Never keep your IP open. Always use username/password or IP whitelisting. An open one is an easy weapon for hackers.
- Encryption: Apply HTTPS. Initially, your system should decrypt the traffic for inspection and then re-encrypt it.
- Logging: In the event of a breach, forensic teams will first check your IP logs.
The Downsides: It’s Not All Perfect
These are some problems with proxy for cybersecurity.
Latency Issues
Each hop prolongs the time. Routing traffic increases the delay by a few milliseconds per request. If you pick a slow location or a not-so-good provider, you are likely to hear complaints from your users.
The “Trust” Problem
You allow the provider to see your internet activity. You have to approve your provider. Don’t use the “freebies” that you come across in forums. Most of the time, these exist solely to steal your data.
Single Point of Failure
If your primary gateway is down, your office’s internet connection will be cut off. So the redundancy is required.
Advanced Tactics: How Does a Proxy Server Work to Protect Your Data?
You might be curious about the specific attack vectors.
Man-in-the-Middle (MitM) Attacks
One can depict a proxy as a managed MitM. It severs the SSL connection, checks the packet contents for viruses, and reconnects. This is the sole method to detect dangers concealed within encrypted traffic.
Geo-Blocking
Scammers usually target specific geographic areas. One could impose geo-based restrictions on the use of proxy for cyber security. If a country is not on your business map, cut off all communications with it.

Cybersecurity and IT Operations
IT teams use these tools for things other than just protection.
- Load balancing: Rather than crashing a single server, spread traffic across the five servers.
- Caching: Reduce bandwidth usage. When 50 workers download the same Windows update, the server downloads it once and then serves it locally to all.
- Anonymity: Security analysts use proxy services for cybersecurity and IT research to survey competitors’ websites or verify copyright infringement without revealing their corporate identity.
Why It is a Non-Negotiable
The threat volume is too high.
Over 2,500 attacks per week were recorded in Q1 2025 alone in the education sector. The retail, finance, and healthcare sectors are constantly under attack.
Proxy for cyber security does not prevent poor passwords from being used or stop an employee from writing their login on a post-it note.
But it enables you to be informed. You regain the advantage. You force attackers to put in more effort. In the security arena, making it hard for attackers is usually enough to drive them to an easier target.
Summary Checklist for Your Strategy
- Audit your traffic: Know what’s happening on your network.
- Choose the right IP: Datacenter for speed, residential for stealth.
- Budget accordingly: The cheap ones leak data. So pay for quality.
- Log everything: What cannot be seen cannot be fixed.
Proxy for cyber security is a basic layer of protection. It removes the noise and opens the gate for the most visible threats. It gives your team the opportunity to address the complex attacks that really matter.
Do not leave your digital front door open. Put a gateway in front of it.